Business Intelligence Knowledge Management and Expert Systems

Expert systems in Artificial Intelligence are a prominent domain for research in AI. It was initially introduced by researchers at Stanford University and were developed to solve complex problems in a particular domain. The following topics will be covered through this blog on Expert Systems in Artificial Intelligence.
- Introduction to Expert Systems in Artificial Intelligence
- Characteristics
- Capabilities
- Components/Architecture
- Expert system technology
- Steps to Develop an Expert System
- Expert Systems Examples
- Traditional System Vs Expert System
- Human System Vs Expert System
- Applications of Expert Systems
- Advantages of Expert Systems
- Limitations of Expert Systems
Our Most Popular Free Courses:
Introduction to Expert Systems in Artificial Intelligence
An Expert system is a domain in which Artificial Intelligence stimulates the behavior and judgement of a human or an organisation containing experts. It acquires relevant knowledge from its knowledge base, and interprets it as per the user's problem. The data in the knowledge base is essentially added by humans who are experts in a particular domain. However, the software is used by non-experts to gain information. It is used in various areas of medical diagnosis, accounting, coding, gaming and more.

Breaking down an expert system, essentially is an AI software that uses knowledge stored in a knowledge base to solve problems. This usually requires a human expert, and thus, it aims at preserving human expert knowledge in its knowledge base. Hence, expert systems are computer applications developed to solve complex problems in a particular domain, at an extraordinary level of human intelligence and expertise.
The Three C's of ES
Characteristics of Expert Systems
- They have high-performance levels
- They are easy to understand
- They are completely reliable
- They are highly responsive
Capabilities of Expert Systems
The expert systems are capable of a number of actions including:
- Advising
- Assistance in human decision making
- Demonstrations and instructions
- Deriving solutions
- Diagnosis
- Interpreting inputs and providing relevant outputs
- Predicting results
- Justification of conclusions
- Suggestions for alternative solutions to a problem
Components/ Architecture of Expert Systems
There are 5 Components of expert systems:
- Knowledge Base
- Inference Engine
- Knowledge acquisition and learning module
- User Interface
- Explanation module

- Knowledge base: The knowledge base in an expert system represents facts and rules. It contains knowledge in specific domains along with rules in order to solve problems, and form procedures that are relevant to the domain.
- Inference engine: The most basic function of the inference engine is to acquire relevant data from the knowledge base, interpret it, and to find a solution as per the user's problem. Inference engines also have explanationatory and debugging abilities.
- Knowledge acquisition and learning module: This component functions to allow the expert systems to acquire more data from various sources and store it in the knowledge base.
- User interface: This component is essential for a non-expert user to interact with the expert system and find solutions.
- Explanation module: As the name suggests, this module helps in providing the user with an explanation of the achieved conclusion.
Our Most Popular Free Courses:
Strategies Used By The Inference Engine
The Inference Engine uses the following strategies to recommend solutions:
- Forward Chaining
- Backward Chaining
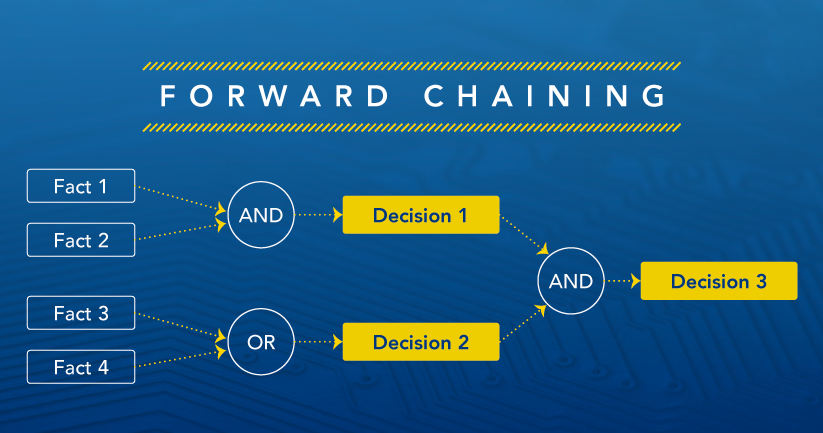
Forward Chaining
With this strategy, an expert system is able to answer the question "What can happen next?"
By following a chain of conditions and derivations, the expert system deduces the outcome after considering all facts and rules. It then sorts them before arriving at a conclusion in terms of the suitable solution.
This strategy is followed while working on conclusion, result, or effect. For example, predicting how does the share market prediction of share market will react to the changes in the interest rates.
Backward Chaining
Backward chaining is used by an expert system to answer the question "Why did this happen?"
Depending upon what has already occurred, the inference engine tries to identify the conditions that could have happened in the past to trigger the final result. This strategy is used to find the cause or the reason behind something happening. For example, the diagnosis of different types of cancer in humans.

Types of Expert System Technology
ES technologies come in various levels, they are:
- Expert System Development Environment
The ES development environment contains a set of hardware tools (Workstations, minicomputers, mainframes), High level symbolic programming languages [LISt Programming (LISP) and PROgrammation en LOGique (PROLOG)], as well as large data bases.
- Tools
Tools, as an ES technology, assists in reducing the effort and cost involved in developing an expert system to a large extent.
- Shells
A Shell an expert system that functions without a knowledge base. It provides developers with knowledge acquisition, inference engine, user interface, and explanation facility. For example – Java Expert System Shell (JESS), Vidwan, etc.
Steps to Develop an Expert System
There are 6 steps involved in the development of an expert system.

Expert Systems Examples
There are numerous examples of expert systems. Some of them are:
- MYCIN: This was one of the earliest expert systems that was based on backward chaining. It has the ability to identify various bacteria that cause severe infections. It is also capable of recommending drugs based on a person's weight.
- DENDRAL: This was an AI based expert system used essentially for chemical analysis. It uses a substance's spectrographic data in order to predict its molecular structure.
- R1/XCON: This ES had the ability to select specific software to generate a computer system as per user preference.
- PXDES: This system could easily determine the type and the degree of lung cancer in patients based on limited data.
- CaDet: This is a clinical support system that identifies cancer in early stages.
- DXplain: This is also a clinical support system that is capable of suggesting a variety of diseases based on just the findings of the doctor.
Traditional Systems versus Expert Systems
A key distinction between the traditional system as opposed to the expert system is the way in which the problem related expertise is coded. Essentially, in conventional applications, the problem expertise is encoded in both program as well as data structures. On the other hand, in expert systems, the approach of the problem related expertise is encoded in data structures only. Moreover, the use of knowledge in expert systems is vital. However, traditional systems use data more efficiently than the expert system.
One of the biggest limitations of conventional systems is that they are not capable of providing explanations for the conclusion of a problem. That is because these systems try to solve problems in a straightforward manner. However, expert systems are capable of not only providing explanations but also simplifying the understanding of a particular conclusion.
Generally, an expert system uses symbolic representations to perform computations. On the contrary, conventional systems are incapable of expressing these terms. They only simplify the problems without being able to answer the "how" and "why" questions. Moreover, the problem-solving tools are present in expert systems as opposed to the traditional ones, and hence, various types of problems are most often entirely solved by the experts of the system.
Human System Vs Expert System
| Human Experts | Expert Systems |
| Perishable and unpredictable in nature | Permanent and consistent in nature |
| Difficult to transfer and document data | Easy to transfer and document data |
| Human expert resources are expensive | Expert Systems are cost effective Systems |

Applications of Expert Systems
| Applications | Role |
| Design Domain | Camera lens designAutomobile design |
| Medical Domain | Diagnosis Systems to deduce the cause of disease from observed dataConduction medical operations on humans. |
| Monitoring systems | Comparing data continuously with observed systems |
| Process Control Systems | Controlling physical processes based on monitoring. |
| Knowledge Domain | Finding faults in vehicles or computers. |
| Commerce | Detection of possible fraud Suspicious transactions Stock market trading Airline scheduling, Cargo scheduling. |
Advantages of Expert Systems
- Availability − They are easily available due to mass production of software.
- Less Production Cost − Production costs of expert systems are extremely reasonable and affordable.
- Speed − They offer great speed and reduce the amount of work.
- Less Error Rate − Error rate is much lower as opposed to human errors.
- Low Risks − They are capable of working in environments that are dangerous to humans.
- Steady response − They avoid motions, tensions and fatigues.
Limitations of Expert Systems
It is evident that no technology is entirely perfect to offer easy and complete solutions. Larger systems are not only expensive but also require a significant amount of development time and computer resources. Limitations of Es include:
- Difficult knowledge acquisition
- Maintenance costs
- Development costs
- Adheres only to specific domains.
- Requires constant manual updates, it cannot learn by itself.
- It is incapable of providing logic behind the decisions.
Expert systems have managed to evolve to an extent that they have stirred various debates about the fate of humanity in the face of such intelligence. Considering that Expert systems were among the first truly successful forms of artificial intelligence (AI) software, it might just be the future of technology.
If your interests are intrigued by the Expert systems in AI, do check out Great Learning's AI courses here.
Further Reading
- Where Will The Artificial Intelligence vs Human Intelligence Race Take Us?
- 10 Hottest Artificial Intelligence (AI) Technologies in 2020 that are Changing the Game
- Top Artificial Intelligence Companies in 2019 And Their Success Stories
- Business Applications for Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- What is Artificial Intelligence? How does AI work, Types and Future of it?
17
Business Intelligence Knowledge Management and Expert Systems
Source: https://www.mygreatlearning.com/blog/expert-systems-in-artificial-intelligence/